Cuprins
- Abstract 3
- Introduction 3
- Analyse the Data 4
- How fine-grained data analysis help in decision-making 8
- Mining customer data 11
- Advantages 11
- Disadvantages 13
- Personal assessment 14
- Reference list 16
Extras din referat
Abstract
This report aims to describe how information systems support management decisions at different levels within organisations and what are the theories, methods and techniques which relate to the design and development of IT solutions.
This paperwork is based on a case to be analyzed and it is structured on the answers to four questions, answers that want to identify market niches in the age of big data.
Introduction
Nowadays, in the evolution of the economy and society, the importance of database systems is constantly growing. Developments in information systems technology have led to an increase in the degree of computerization of many applications in various business areas. Data has become a resource in many organizations and thus, accessing it efficiently, distributing it, extracting information and creating a system capable of managing it effectively, have become more than urgent needs.
For a long time, database systems were exclusively the responsibility of IT specialists. Currently, the use of databases has become accessible to all computer users.
Analyse the Data
As a simple definition, Data are ”information, especially facts or numbers, collected to be examined and considered and used to help decision-making, or information in an electronic form that can be stored and used by a computer”. (Anon., 2020).
In other words, data is raw material divided in different forms (numbers, characters, symbols, images, sounds, electromagnetic waves, bits) that are being recorded and stored, and so knowledge are created. (Kitchin, 2014).
As Kitchin (2014) sustains, some data (numbers) can be easily organised, stored and analysed using calculus and algorithms, but some data are irregular, with an undefined structure (narrative text, photos, videos) and these can be stored and analysed using advanced databases and machine learning techniques.
Data can be generated either by capturing them directly from sources (surveys, observations, cameras, scanners, laboratory experiments, recordings), or are inherently produced by devices and systems.
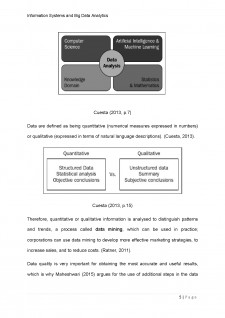
According to Cuesta (2013), data analysis is a process in which organized data will be used to explain what happened and predict the future, so is about making questions and developing explanations. To do that, data analysis combines computer science, artificial intelligence and machine learning, statistics and mathematics, and knowledge domain.
Bibliografie
Anon (2020). Cambridge Dictionary [Online] Available from: https://dictionary.cambridge.org/dictionary/english/data. [Accessed 2nd of January 2021].
Anon (2020). Educba [Online] Available from: https://www.educba.com/advantages-of-data-mining/?source=leftnav. [Accessed 3rd January 2021].
Bocij, P., Greasley, A. and Hickie, S. (2018). Business Information Systems: Technology, Development and Management for the Modern Business. 6th ed. Harlow: Pearson Education Limited.
Cuesta, H. (2013). Practical Data Analysis. Birmingham: Packt Publishing Ltd.
Ilmudeen, A. and Bao, Y. (2018). Mediating role of managing information technology and its impact on firm performance: Insight from China. Industrial Management & Data Systems. [Online] 118(4), pp.912-929. Available from: https://www-emerald-com.ezproxy.bolton.ac.uk/insight/content/doi/10.1108/IMDS-06-2017-0252/full/pdf?title=mediating-role-of-managing-information-technology-and-its-impact-on-firm-performance-insight-from-china. [Accessed 9th January 2021].
Kitchin, R. (2014) The Data Revolution: Big Data, Open Data, Data Infrastructures and Their Consequences. London: SAGE Publications Ltd.
Laudon, K.C. and Laudon, J. (2018). Essentials of MIS. 13th ed. Harlow: Pearson education Limited.
Maheshwari, A. (2015). Business Intelligence and Data Mining. New York: Business Expert Press.
Nettleton, D. (2014). Commercial Data Mining: Processing, Analysis and Modeling for Predictive Analytics Projects. Waltham: Elsevier.
Ratner, B. (2011). Statistical and Machine-Learning Data Mining: Techniques for Better Predictive Modeling and Analysis of Big Data. 2nd ed. Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Sarabi, A., Naghizadeh, P., Liu, Y. and Liu, M. (2016) Risky business: Fine-grained data breach prediction using business profiles. Journal of Cybersecurity, [Online] 2(1), pp.15-28. Available from: https://academic.oup.com/cybersecurity/article/2/1/15/2629555?login=true#. [Accessed 11th January 2021].
Schmarzo, B. (2015). Big Data MBA: Driving Business Strategies with Data Science. Indianapolis: John Wiley & Sons.
Preview document
Conținut arhivă zip
- Identifying Market Niches in the Age of Big Data.docx